Computer-aided design (CAD) programs are specialized software packages designed to assist in the creation, planning, production, and/or communication of designs. Computer-aided design was initially developed to employ the use of computers to expedite the production of 2D technical drawings for electronics or to control specialized cutting equipment (CNC).
A Brief History Of CAD
Sketchpad: An Early CAD (1963)
The software demonstrated below is regarded as one of the most influential advances in computer-aided design and human-computer interaction. This software allows the user to geometric forms (lines, circles, arcs) and their relationship to one another (tangent, coincident, etc.). The pointer interface was ahead of its time, although it was quickly replaced superseded by the mouse in the late 60s.
Computer-aided design allows users to:
- Make changes to the size & scale of drawings and objects
- Reference other designs
- Modify the features of the design
- Produce drawings from designs
- Communicate with computer-controlled equipment
How Is CAD Different Than Other Graphics or 3D Programs?
CAD is designed to manipulate points, lines, arcs, curves and other geometric objects by their coordinates (their position in relation to an origin). In 2D space, this origin is 0,0. In 3D space, this origin is 0,0,0. CAD includes tools to describe how geometry are related to each other. For example, two circles may need to remain equal in size throughout the design. Graphics editing software provides tools focused toward changes in colour representation. Although there are many similarities, generally speaking CAD is considered in manufacturing, architecture & building-information management, rending, drafting, and modeling.
Mesh modeling software, such as Blender, is also not generally considered CAD. Although Blender may perform similar functions to fully-featured CAD programs, the paradigm and intended use is different. Mesh modeling emphasizes the manipulation of individual or groups of vertices, edges, and faces in 3D space. Although still considered a form of technological design, this non-CAD form of design is widely used in organic modeling or video game assets, animation, and creative rendering.
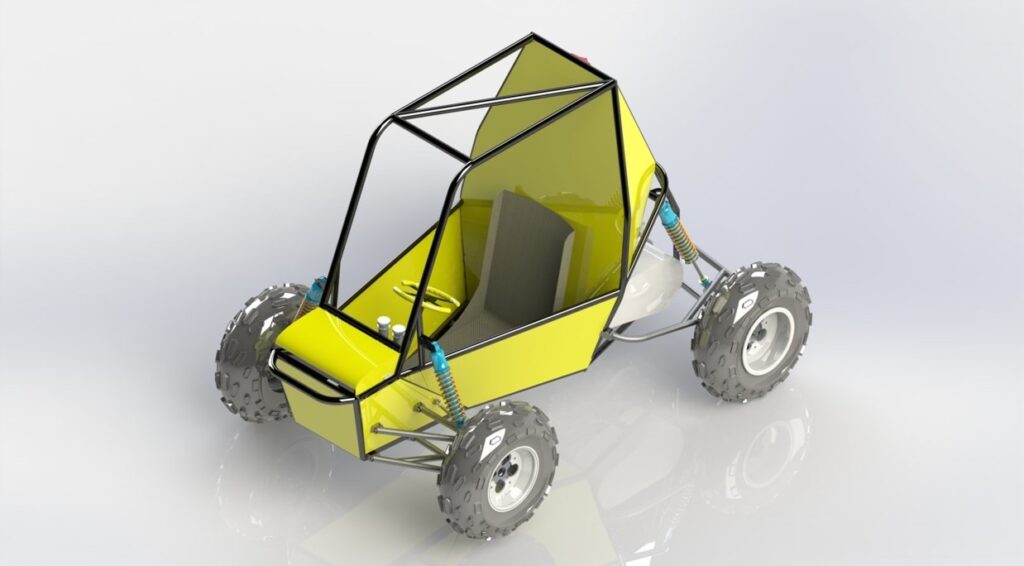
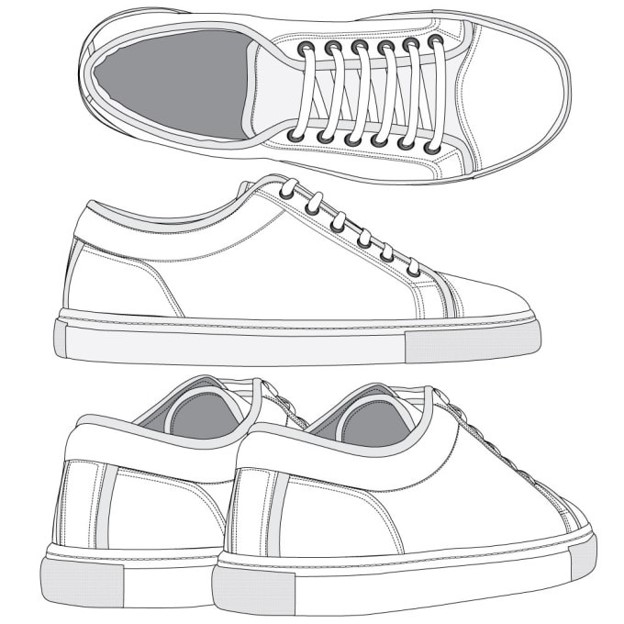
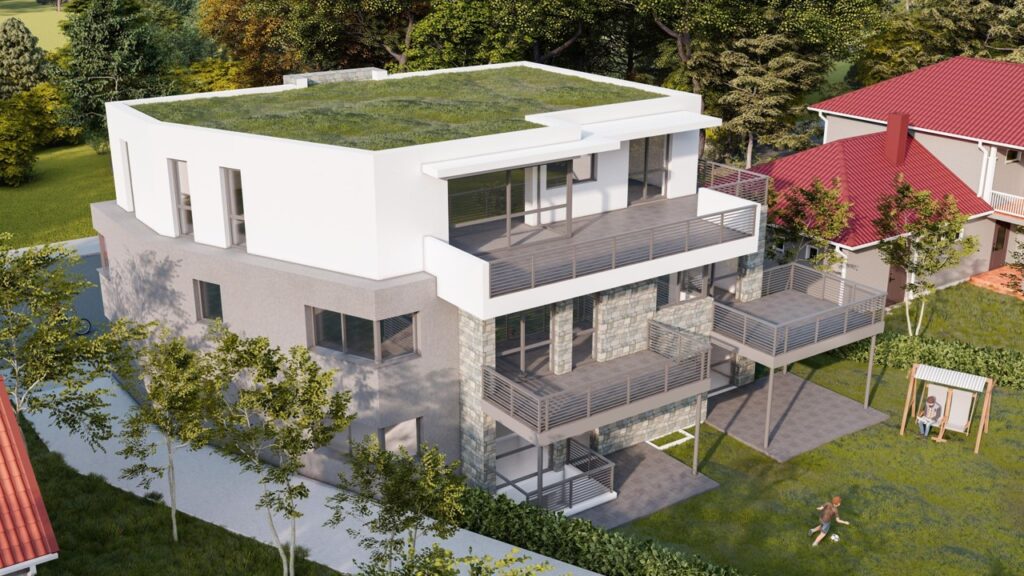
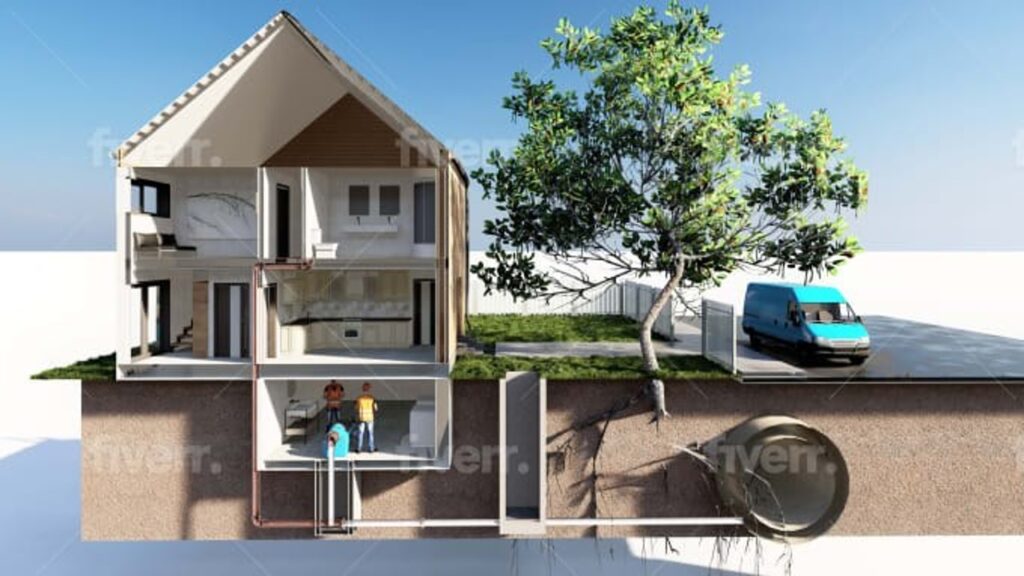
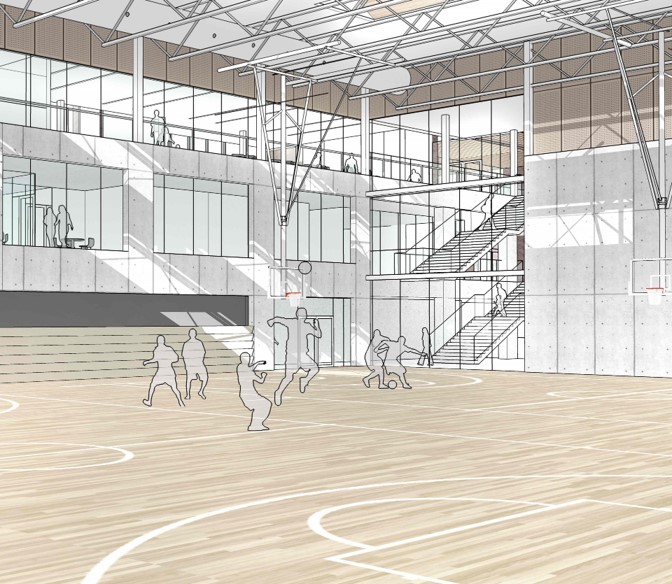
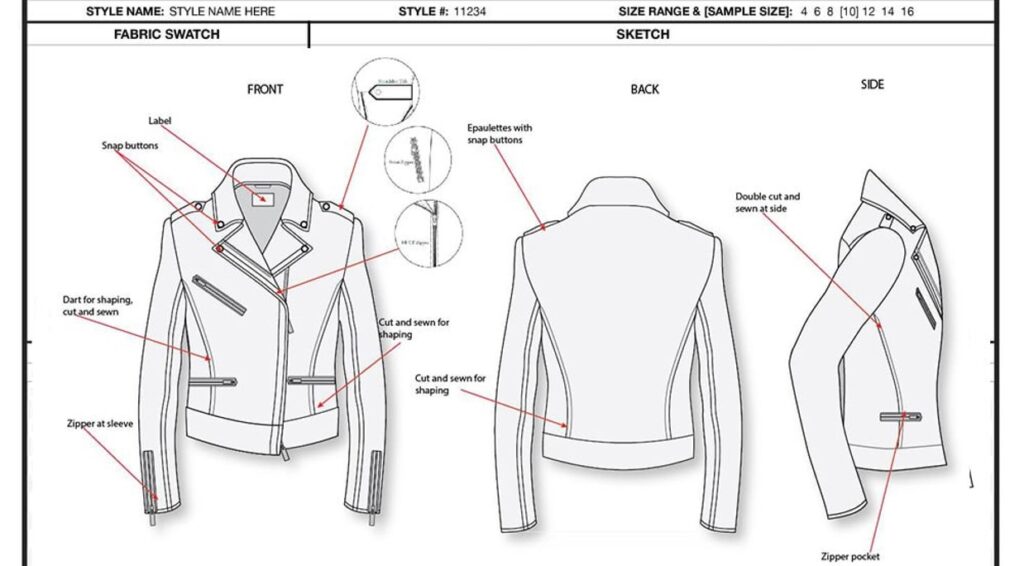
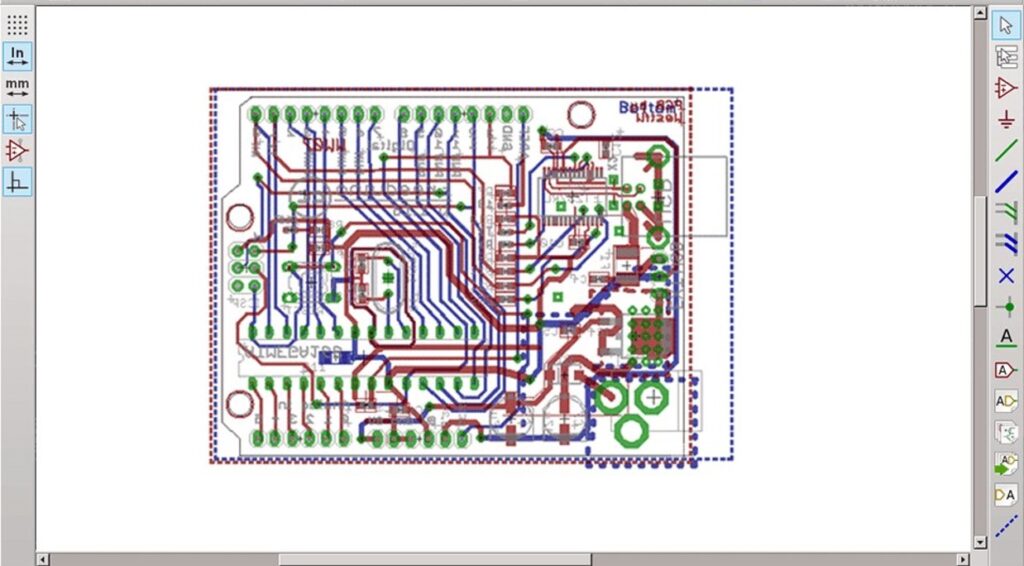
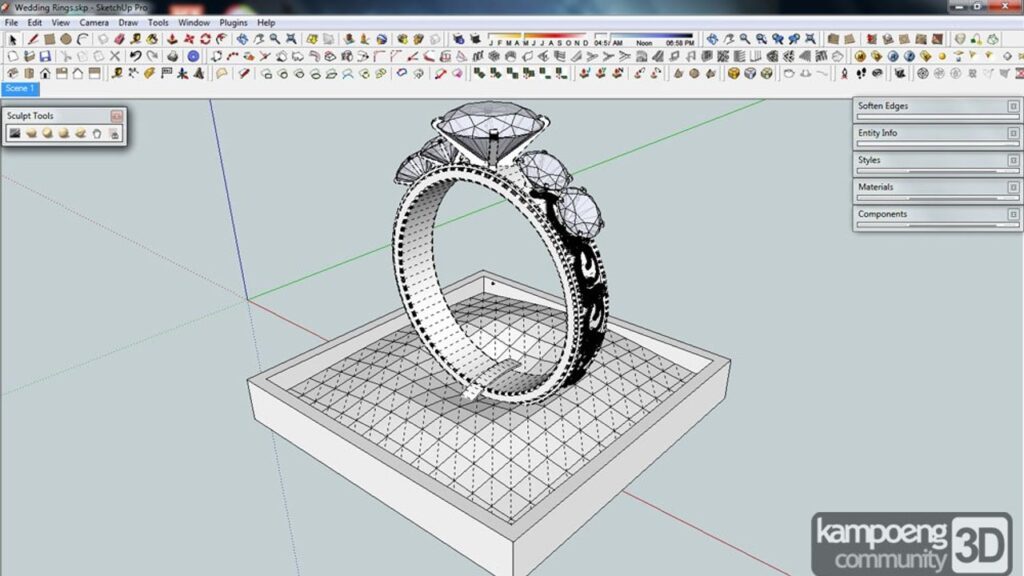
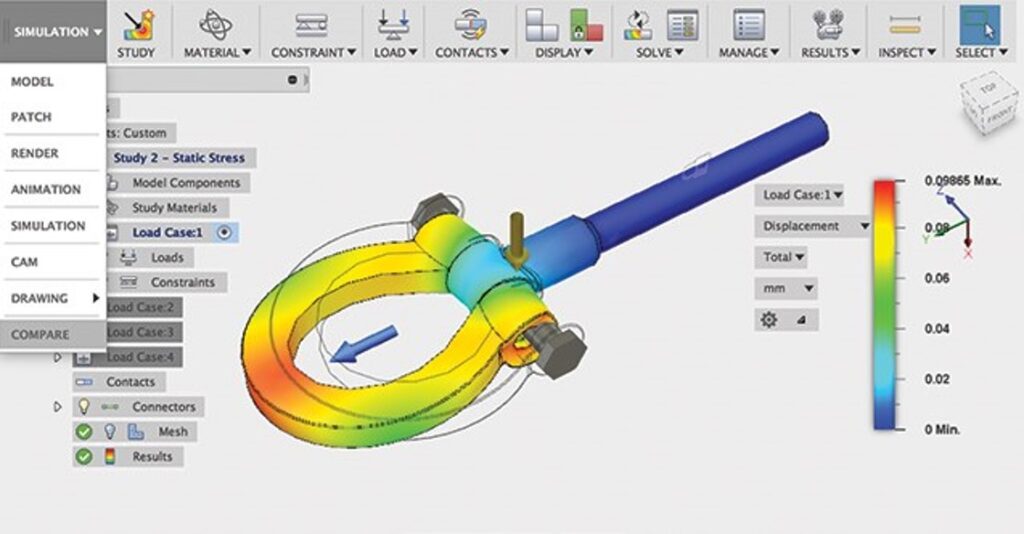
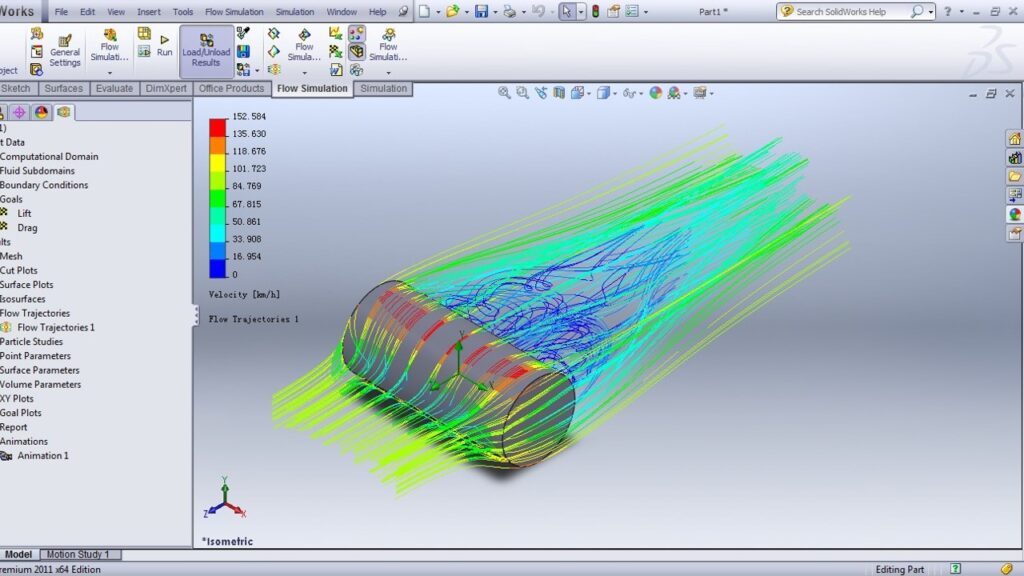
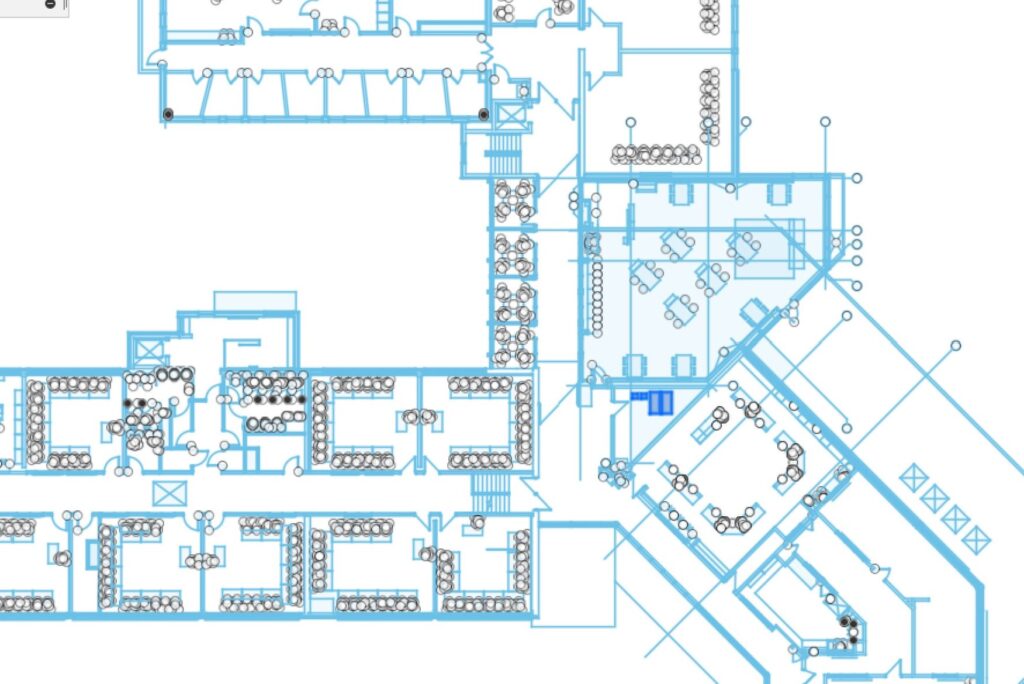
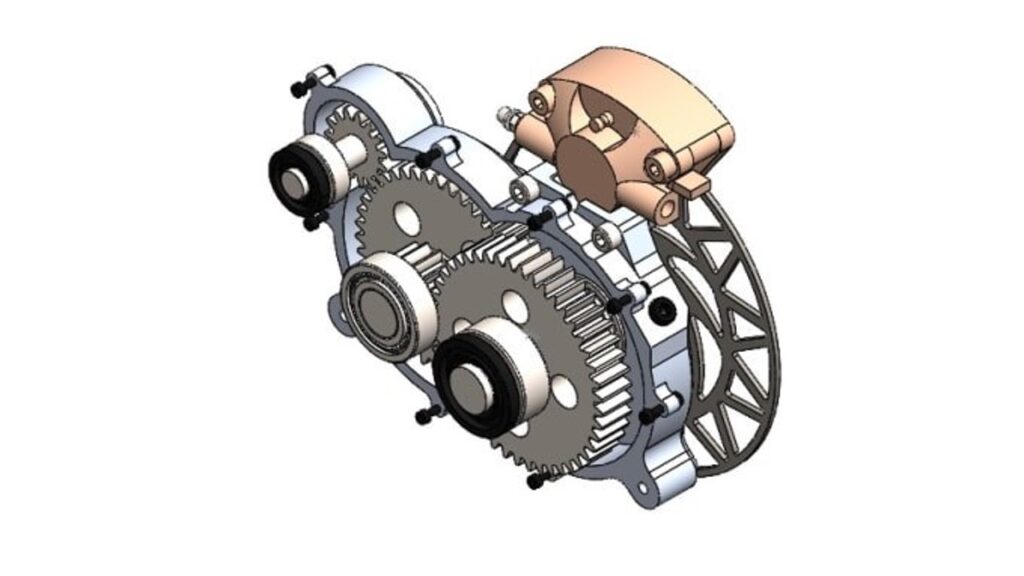
Examples of CAD In Use